Potatoes provide a diversity of culinary applications. From the crunch of french fries to the semi-liquidy texture of mashed potatoes, they are proficient in sustaining satiety. Potatoes are a staple diet in many regions of the world, particularly Ireland. They have a significant contribution to the economic stability of such regions. A lot of fiber in potatoes brings about the feeling of fullness or satiety when we consume them. Potatoes are the culinary chameleons; they can be molded into any dish. Nutritional content and flavor vary according to the cooking method.
Baked or boiled potatoes preserve more flavor and nutritional value. Fried or properly cooked potatoes are crunchier and usually spicier than the former. No matter how you cook them, they still contain fiber, vitamin C, folate, and resistant starch, which make them a healthy staple.
Historical Popularity of Potato
According to historians and researchers, potatoes were first cultivated in the Andean region of South America. The Andes is a high-altitude mountainous region that provides a suitable habitat for the growth of potatoes. Incas, the indigenous civilization at that time in the Andes, cultivated potatoes and introduced their dietary importance to the world. Sir Walter Raleigh was the one who let Europe become familiar with this nutritious staple. Potatoes were brought to Europe in the 16th century during the Columbian Exchange. At first, they didn’t get popular and were considered poisonous. Then, with the advent of time, people began to recognize their nutritional advantages and ergo, they become a versatile vegetable.
Nutritional Content of Potatoes
Although they contain a diversity of nutrients, the following nutrients are most significant in imparting health benefits.
Vitamin C
Potatoes serve as a good source of vitamin C. Vitamin C is crucial for boosting immunity and directing white blood cell production. It does so by playing a contributory role in the differentiation of stem cells into immune cells. Vitamin C also serves as an anti-oxidant, combating oxidative stress. Phagocytic vitamin C is prominent in sustaining immune and skin health.
Potassium
A healthy heart needs potassium to beat properly. Potassium helps prevent arrhythmias by maintaining the electrical activity of the heart. Potassium supports heart health, muscle functioning, and electrolyte balance. Potatoes provide an adequate quantity of potassium. Being a crucial electrolyte, potassium plays a critical role in upholding the osmotic tension and distribution of electrolytes.
Antioxidants
Potatoes contain anti-oxidants that safeguard the body’s internal environment against reactive species. Harmful molecules such as reactive oxygen species and free radicals impose an unstable environment on the cellular structures. Antioxidants stabilize the free radicals and prevent the body from oxidative stress.
Reasons Behind Potatoes Satiety
Dietary Fiber
Potatoes are a rich source of dietary fiber, both in their skin and content. Fiber fosters gut health and improves the sustainability of gut microbiota and the inner layer of the gut. Dietary fiber is obtained from plant-based foods such as potatoes, legumes, fruits, and other vegetables. It can be soluble or insoluble. Soluble dietary fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like consistency. While insoluble dietary fiber assists bowel movement. Dietary fiber is simply the roughage or indigestible plant material that provides bulk for the movement of food in the intestines.
Resistant starch
The resistant start is the type of starch that is resistant to digestion in the small intestine, similar to dietary fiber. Resistant starch is present in starch foods such as potatoes, legumes, nuts, seeds, grains, etc. Resistant starch prevents its digestion and reaches the colon. It behaves like dietary fiber in promoting gut health and fulfilling the appetite.
How do dietary fiber and resistant starch contribute to Satiety?
Satiety is the feeling of fullness or satisfaction. Dietary fiber and resistant starch provide bulk to the ingested foods and support the movement of undigested food to the colon. In the colon, they promote the gut microbiome by providing a favorable environment for the production of healthy microorganisms. Moreover, they fortify the intestinal barrier to impede the entry of harmful microorganisms into the gut. Microbiota in the colon ferments the fiber and resistant starch into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) have beneficial roles in the endurance of the gut. Their ability not to digest promptly imparts a feeling of satiety.
Resistant starch and fiber help in weight management by imparting satiety. Soluble fiber and resistant starch regulate the blood sugar levels by slow degradation of interconnected fibers. Thus, potatoes are perfect for diet due to their high carbohydrate content that provides both flavor and satiety in a single dish and with less quantity.
Low in fats and calories
Potatoes are low in fats and calories, whereas high in carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body and provide satiety. Potatoes, being lower in calorie content and rich in starchy content, are perfect for gut health and flavor.
According to Jamieson Brothers ( a Scottish company supplying high-quality potatoes), potatoes contain 33% of vitamin C, 9% potassium, 15g of starch, 2.2g of dietary fiber, and 0.1g of fats per 100g.
Amazing facts about Potatoes (Some Side Information)
Potatoes have a lot of amazing facts, but following only two are discussed.
Genetic similarly
Humans and potatoes share a striking genetic similarity of 99.9%. This is a surprising fact and a confusing one. How potatoes and humans are genetically so similar? What can be the reason for this? Maybe due to regional or cultural origins. If you know the reason for this, let us know in the comment section.
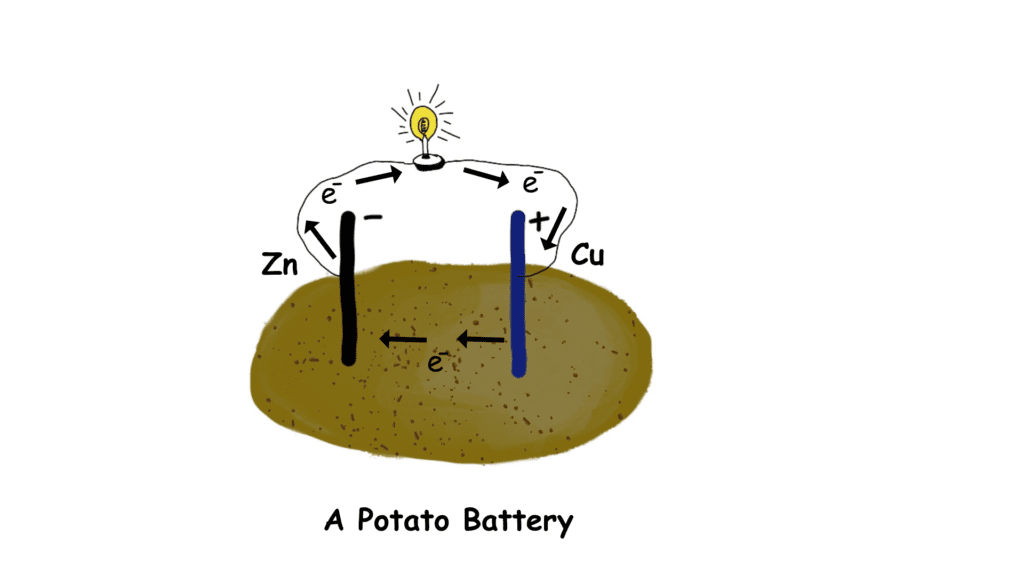
Potatoes and electricity
Yes, this is indeed a surprising fact about potatoes. Starch present in potatoes can behave as an electrolyte and turn potatoes into a little cell or a battery that can generate electrical current. Two electrodes that have the potential to transfer electrons according to the electrochemical series, can assist the starch solution as an electrolyte. Although the voltage generated is not so high, but can operate a small light bulb or an LED device.