It may seem miscellaneous why medications cause the bladder to hold pee. It can be a leg up in some conditions such as involuntary micturition or incontinence. But, most of the time, the retention of urine within the bladder is not the target. Urine retention can occur as a side effect of the consumption of certain medications. There will be a thorough understanding of such types of medications and how they indirectly affect bladder contraction. Although urine retention is not as inconvenient as incontinence, it can be painful and can have drastic effects. Too much relaxation of the bladder muscles is the leading cause of urine retention inside the bladder.
Background Study of The Urinary Bladder Receptors
Understand the Location and Function of The Urinary Bladder
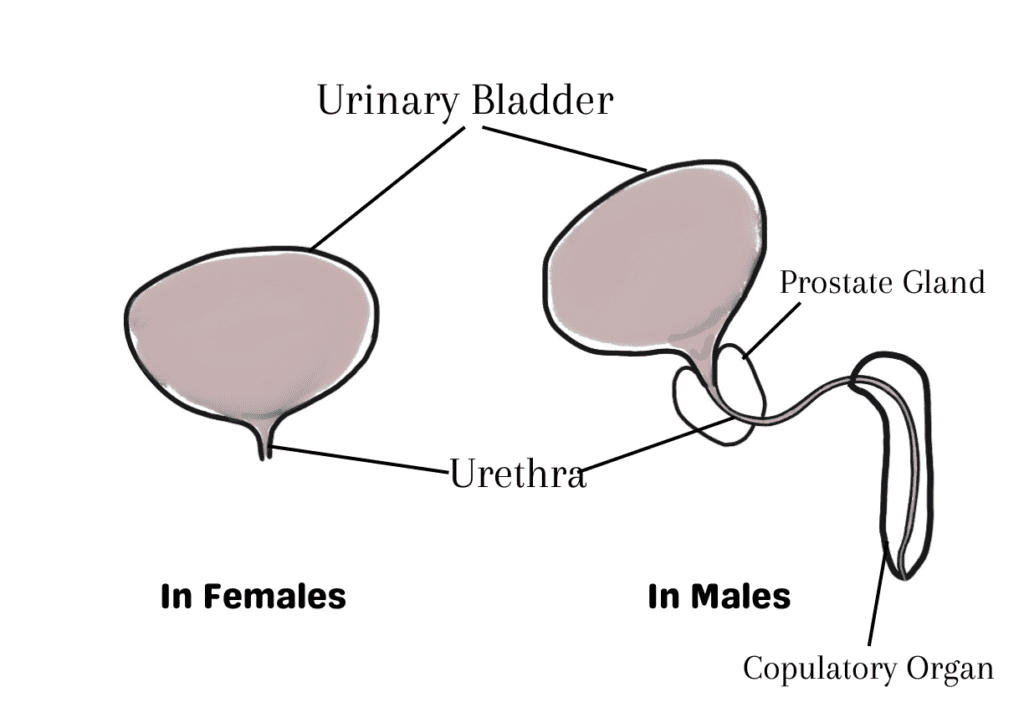
The urinary bladder is a hollow organ, that functions in the storage of urine. Kidneys release the urine through ureters into the urinary bladder. The location and delivery of urine is a little bit different in different genders. In females, the urinary bladder directly empties itself to the outside of the body through the urethra. Urthera is in the upper side of the vagina in females. In males, the urine from the urinary bladder travels through the urethra to the copulatory organ. In males, the urethra is comparatively long as it carries the urine all the way from the urinary bladder to the opening in the glans penis.
Type of Receptors At The Urinary Bladder
The urinary bladder has numerous receptors either in its outer layer or its smooth muscular layer. Most blunt responses of urinary contractions are related to the receptors, present at the smooth muscle cells. A urinary bladder contains the following types of receptors. There can be further receptors present in the urinary bladder, but these are the most active ones in the study of urinary retention.
- Cholinergic Receptors (Muscarinic Receptors)
- GABAergic Receptors
- Adrenergic Receptors (most interesting ones, at the last)
- Serotonergic Receptors
- Neurotrophic Receptors, etc.
Among all of these receptors, we will discuss the cholinergic receptors, GABAergic receptors, and adrenergic receptors in detail. These receptors have a commanding presence to certain medications that affect the urinary bladder contractions.
Type of Medications That Can Cause Urinary Retention
Going respectively with the type of receptors, following medications can have indirect effects on the retention of urine Inside the bladder.
1. Anticholinergic Medications
Anticholinergic medications target the acetylcholine receptors, also called cholinergic receptors in the body. Cholinergic receptors can be muscarinic or nicotinic. The urinary bladder has muscarinic-like receptors that belong to the class of cholinergic receptors. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter or chemical that activates the physiological responses of cholinergic receptors. In the urinary bladder, cholinergic receptors provoke the contraction of the bladder detrusor muscles. In the cases of persistent activation of cholinergic receptors, it results in the involuntary release of urine due to excessive contractions of the bladder muscles. The same case happens in nerve gas poisoning.
So, medications that can hinder the activity of cholinergic receptors are called anticholinergic medications. These medications do not have the target to cause urinary retention. However, due to the systemic effects of anticholinergics, they may also affect muscarinic receptors in the bladder muscles. Such a condition results in the relaxation of urinary bladder muscles. This symptom is also prominent when patients take an anticholinergic medicine; atropine. Anticholinergics have potential benefits for certain heart and lung abnormalities, particularly bradycardia and bronchoconstriction. So, when patients take anticholinergics to target specific organs, they may also affect the bladder muscles and cause urinary hesitancy.
2. GABAergic Medications
GABAergic medications stimulate the activity of GABAergic receptors throughout the body. The brain has GABAergic receptors whose stimulation can bring about the symptoms of delusions and muscle relaxations. GABAergic medications follow the same philosophy while working throughout the body. Most sedatives can cause the amplification of GABAergic receptors. Although the target of GABAergic medications is always CNS, these medications can also galvanize the receptors in the peripheral nervous system, including those that are present in the bladder.
The urinary bladder has two subtypes of GABAergic receptors; GABAA and GABAB.
Both have different working mechanisms and chemical structures. But their physiological effects on the urinary bladder are similar; causing the relaxation of smooth muscle cells (detrusor muscle cells) of the bladder.
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a neurotransmitter (more specifically, inhibitory neurotransmitter) for GABAergic receptors. GABAergic receptors cause muscle relaxation by stimulating the release of GABA from synaptic endings. Furthermore, GABA receptors also induce ionic changes such as efflux of potassium ions and checking the influx of calcium ions. As potassium ions make the internal environment positive, assisting depolarization, its excess efflux may cause instability in the positive internal environment. Similarly, calcium ions bring about muscle contractions. When GABA receptors check the calcium entry inside the cells, they potentially affect the contractile activity of muscles.
GABAergic medications have different modes of action. Some GABAergic medications overstimulate the production of GABA, some cause the under regulation of GABA breakdown, and some may contain chemicals that mimic the structure of GABA. In such ways, GABAergic medications boost the physiological effects of GABAergic receptors. Patients may experience problems with urination as a consequence of taking GABAergic-stimulating medications.
A scientific study by the University of Calgary published in the CPT pearl of the week clarifies the effects of medicines on the urinary bladder receptor. This explains how anticholinergic, GABAergic, and adrenergic medications can cause urinary retention.
3. Adrenergic Medications
Adrenergic receptors can be alpha-adrenergic or beta-adrenergic, depending upon the location and physiology of receptors. The urinary bladder contains both alpha-adrenergic receptors and beta-adrenergic receptors. Their location on the urinary bladder varies and alpha-adrenergics have more scope in the situation of urinary retention.
A Thorough Explanation of The Locality of Adrenergic Receptors
Adrenergic receptors are found in the heart, lungs, smooth muscle cells of blood vessels, uterus, urinary bladder, eyes, and more. Alpha-adrenergic receptors, either alpha1 or alpha2 are more operational in the contraction of smooth muscle cells. These receptors lead to vasoconstriction in less preferable areas of the body. Alpha1 -adrenergic receptors are those whose activity affects the urine release. The bladder neck and prostate gland (in males) contain alpha1-adrenergic receptors. They have a characteristic role in contracting the bladder muscles.
Beta-adrenergic receptors are less preeminent in the urinary bladder contractions. They have more blunt roles in the heart, the lungs, the metabolism, dilation of blood vessels. They act somewhat in contrast to alpha-adrenergic receptors in the body. Where alpha-adrenergic receptors are more synchronized with the constricting mechanisms, they have clear effects in dilating the blood vessels. Beta-adrenergic receptors present in the heart raise blood pressure and cardiac output. It helps to deliver maximum oxygen to the essential body regions.
Alpha-adrenergic receptors’ vasoconstriction targets the organs whose activity is not so essential. At the same time, beta-adrenergic receptors work more to deliver all the available oxygen and nutrients to the most needy regions, the brain, heart, lungs, kidneys, etc. The question of the urinary bladder is in the non-essential regions in the sympathetic nervous system. Moreover, beta-adrenergic receptors in the lungs cause bronchodilation, opening the airways to inhale the maximum amount of oxygen. They cause the relaxation of urinary bladder muscles to reserve water in the body.
How do Adrenergic receptors Synchronize With The Sympathetic Nervous System?
There can be a question that why adrenergic receptors are doing these operations in the body. For what they are preparing the body? Let’s see this interesting mechanism in detail.
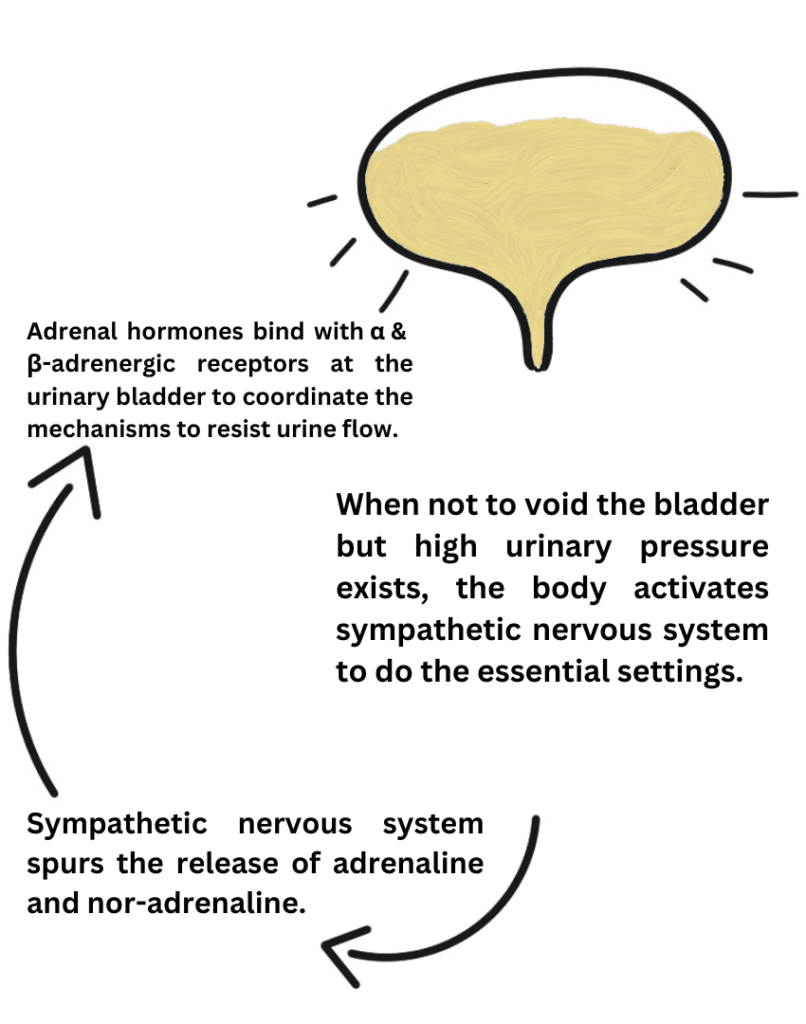
Adrenergic receptors palpitate towards adrenal glands secretions; adrenaline and nor-adrenaline. Both of them are the special hormones of the sympathetic nervous system. It is conceivable from its name that, the sympathetic nervous system optimizes the body’s conditions by showing sympathy to the body. In the presence of any abnormal stimulus, or more excitatory than the routine stimuli, trigger the wire of the sympathetic nervous system.
All of the hard work of adrenergic receptors do is to make the body a full more solid to combat stress situations. Here, stressful situations don’t only mean psychological stress. It can be mechanical stress, as in the case of tough and persistent exercise. It can also be due to an imbalance in the external homeostatic situations. Ergo, to combat any situation that is not in the routine, incites the sympathetic nervous system.
The following details can explain how the above-mentioned effects of adrenergic receptors synchronize with the sympathetic nervous system;
- Bronchodilation makes a person inhale effortlessly as the body needs more oxygen in low-energy situations.
- High blood pressure can be deadly in steadfast activation. But, for fixing stress conditions, high heart activity produces more cardiac output to enhance the perfusion of blood in the tissues and organs.
- Vasoconstriction of certain regions provides more blood volume for vital body organs. Vasodilation assists those vital organs.
There are many other effects of adrenergic receptor activation on the sympathetic nervous system. But, these were the main reasons behind the use of adrenergic medications.
How do alpha-adrenergic medications and beta-adrenergic medications cause the bladder to hold pee?
Alpha-adrenergic receptor boosters boost the contractile activity of detrusor muscles in the urinary bladder. Alpha-adrenergic boosters relive nasal congestion and and aid in the elevation of blood pressure. They have vasoconstricting effects in managing these conditions. Such medicines can cause the urinary bladder muscles to contract enough so that they may cause urinary obstruction. Urinary obstruction arises as a systemic effect of alpha-adrenergic boosters. This is not a normal process with the use of alpha-adrenergic boosters. However, this condition can arise due to its potential to cause excessive bladder muscle contractions.
On the contrary, beta-adrenergic receptors cause smooth muscle dilation in the bladder as these receptors are more associated with vasodilation. The philosophy behind this dilation is to lessen the urgency of urination when it is not the appropriate time to urinate. The urgency of urination and the mind making the body not urinate is also a kind of stress stimulus for the sympathetic nervous system. For this physiology, beta-adrenergic receptors relax the bladder walls and make the urgency low to some extent. This is the normal physiology of beta-adrenergic receptors in the control of urine.
But, when a person takes beta-adrenergic receptor blockers for relieving hypertension, it may also block beta-adrenergic receptors in the bladder muscles. While beta-blockers appreciably reduce the blood pressure by reducing the heart rate and contractility, they have mysterious effects on the urinary bladder muscles. The mechanism is somewhat complex, but beta-blockers further cause the relaxation of urinary bladder muscles in some individuals. More relaxation of the urinary bladder muscles makes it difficult for the bladder to contract appropriately and voiding the bladder. The effect of these modifications is the progression of urinary retention in the bladder.
Beta-blockers do not potentially cause urinary retention as alpha-stimulators do. Alpha-stimulators are more observable with impact on the bladder muscles as compared to the beta-blockers. Beta-blockers have very minimal effects (if observable) on the urinary retention. Individuals with pre bladder dysfunctions are at the edge to be affected by them.
Seek a Professional Advice
The purpose of this blog is to just provide information about certain types of medications that can affect the contraction and relaxation of the urinary bladder muscles. It is not obligatory that the use of such medications would cause the bladder to hold pee in the first place. Most commonly, urinary retention occurs as a side effect of the usage of such types of medications. If someone is experiencing urinary retention while taking these medications, he should seek professional advice from a medical doctor or healthcare consultant. It is also a fact that such side effects only arise in some individuals.




