Fat metabolism is both a healthy alternative and an upsetting mechanism simultaneously in the realm of type 2 diabetes. Energy production and weight loss run side by side in fat metabolism during insulin insensitivity. The body needs energy for its sustenance. Metabolic reactions occur inside the body and provide chemical energy. Cells break down the chemical molecules to gain energy from them. Glucose is the primary fuel for energy production. The body converts every carbohydrate we eat into glucose. Glucose contains 6 carbon atoms, 6 oxygen atoms, and 12 hydrogen atoms.
C-H bond breaks with sufficient energy for catalyzing the metabolic activities within cells. In type 2 diabetes, cells are immune to insulin. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone, secreted by the pancreas. Insulin spurs the cells to utilize glucose as the fundamental source of energy. In this way, it also lessens the glucose levels in the bloodstream. In type 2 diabetes, cells do not respond to insulin and are unable to absorb glucose from the blood.
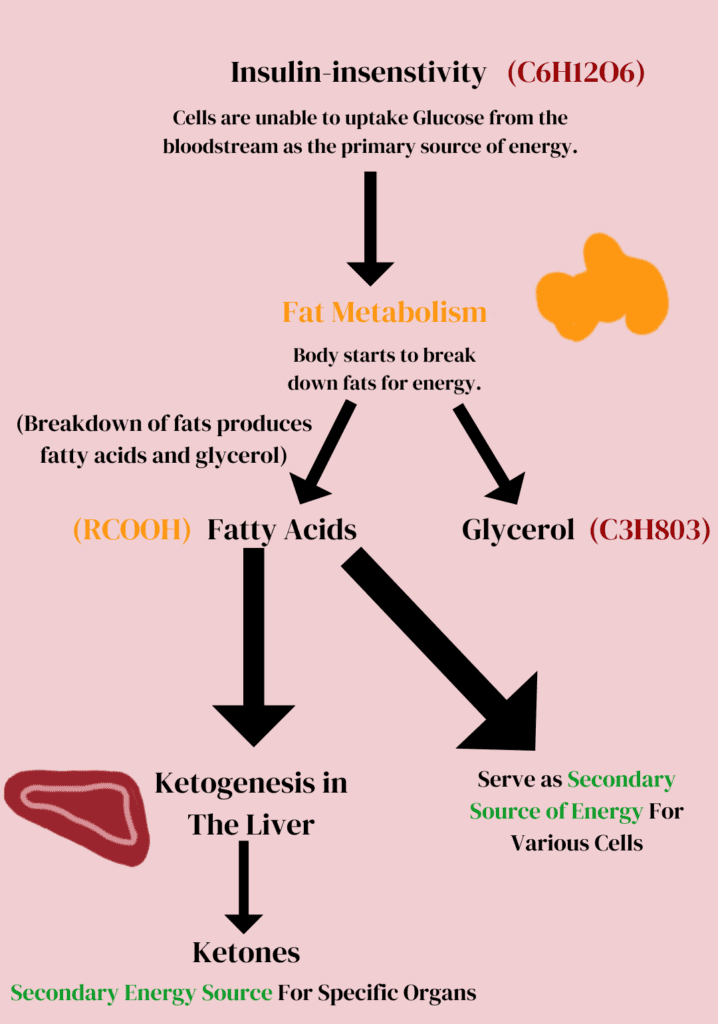
Henceforth, blood glucose levels rise and affect glucose management. When cells are restricted to glucose uptake, the body perceives this as an energy-deficient signal. For this reason, it shifts to fat metabolism to fulfill the energy demands of the body.
Fat Metabolism Results in the Ketone Production
Lipolysis (breakdown of fats) is the alternative source of energy. Fatty acids obtained from fat metabolism are converted into ketone bodies in the liver. Ketones serve as an impressive source of energy for certain organs notably the brain, heart, and muscles. Apprehend the process in an understandable way.
Insulin-insensitivity in Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas secrete insulin but the insulin cannot effectively enhance glucose absorption in cells. Blood glucose levels rise as cells become insensitive to glucose. The body perceives this as a shortage of glucose and a lack of respiratory fuel. Mitochondria utilizes glucose in cellular respiration to generate chemical energy in the form of ATP. ATP is the foremost source of energy as phosphate bonds yield a greater deal of energy when broken.
Fat Metabolism – An Alternative Source of Energy
To provide energy to the body for necessary metabolism, it switches to fat metabolism. Fat metabolism is the breakdown of fats into fatty acids and glycerol. Under stress conditions or in the case of low energy production, adrenal glands release epinephrine (adrenaline). Epinephrine activates lipase enzymes to carry out lipolysis. Resultantly, fatty acids and glycerol are produced. Fatty acids serve as an energy source for various body cells and tissues. In type 2 diabetes, the same scenario occurs and the patient starts to lose weight. Weight loss is the major complication in type 2 diabetes because of fat metabolism.
Ketogenesis in The Liver
Some cells and organs demand ketones instead of fatty acids as an energy source. For this purpose, the liver initiates the conversion of fatty acids into ketones. Ketogenesis in the liver involves complex mechanisms. Fatty acids are first converted to acetyl CoA by a process called beta-oxidation. Acetyl CoA then enters into the citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle in liver mitochondria. Due to the surplus of acetyl CoA in the liver, it converts the excess acetyl CoA into ketone bodies. Hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone are the main ketones obtained from the metabolism of fatty acids in the liver.
Significance of Ketone Production
Ketones serve as the secondary source of energy in the shortage of glucose. In type 2 diabetes, glucose is not in less amount but the cells are unable to absorb it. Fatty acids and ketones act as significant sources of energy when glucose cannot be consumed. Ketones, namely hydroxybutyrate can cross the blood-brain barrier and prove an excellent source of energy for neural health. However, in type 2 diabetes, excess fat metabolism leads to severe complications such as weight loss and impaired glucose management.
In normal circumstances, fat metabolism is a beneficial phenomenon when occurs within control. In the insulin-insensitivity case, the body metabolizes fats instead of glucose. This metabolism leads to elevated fatty acid concentration in the blood. Surplus glucose and fatty acids in the blood further agitate type 2 diabetes.
The relation of SGLT2 Inhibiters and Diabetic Ketoacidosis
SGLT2 inhibitors are used as a medication for type 2 diabetes. They limit the reabsorption of glucose from renal tubules back into the blood. SGLT2 inhibitors have a diuretic effect due to their glucose retention actions within kidney tubules. Consequently, blood glucose levels decrease which is further aggravated by insulin insensitivity in type 2 diabetes. The body switches to fat metabolism for energy synthesis by the phenomena described above. So, SGLT2 inhibitors are indirectly related to the production of ketones (in the case of fat metabolism for energy production). As the production of ketones is associated with diabetes, it is called diabetic ketoacidosis.
Multiple studies have suggested the indirect relation between SGLT2 inhibitors intake and the elevated levels of ketones in the blood.