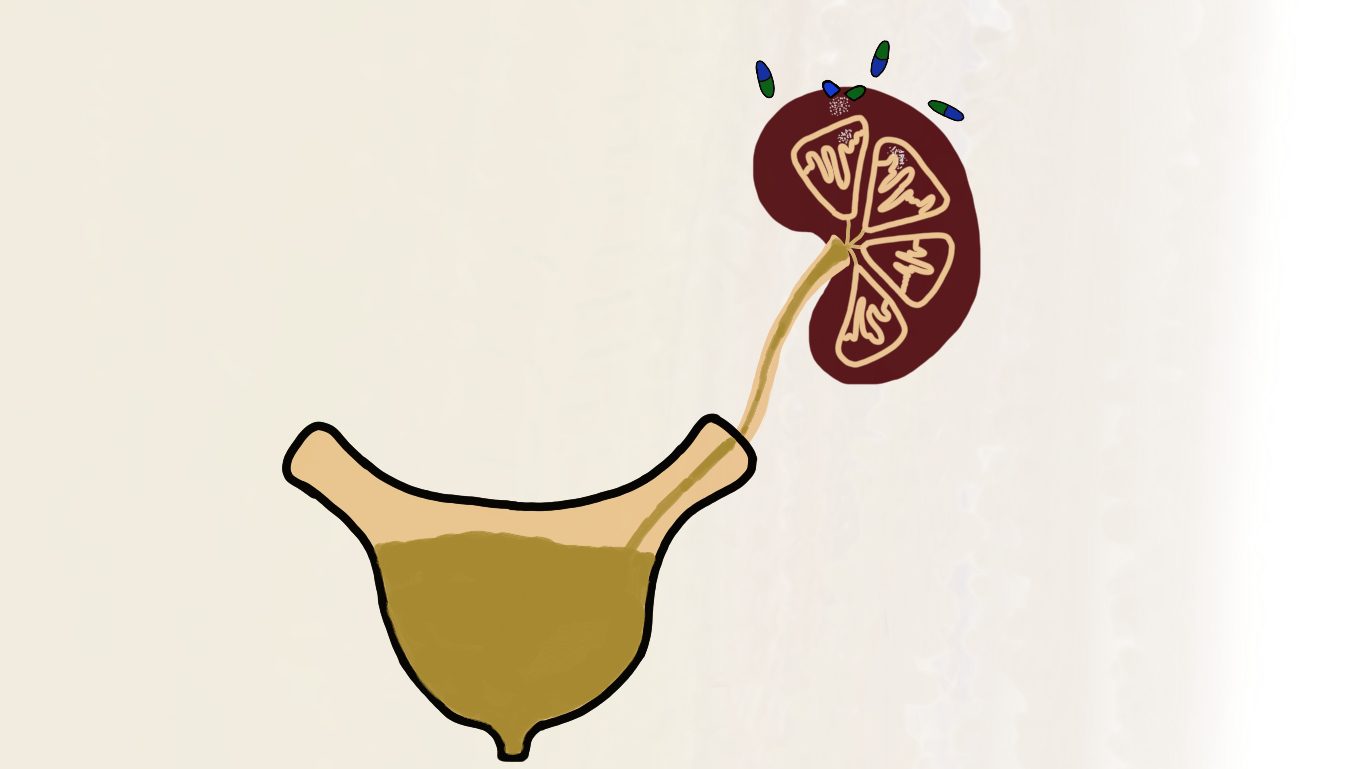
Not all diabetic medicines have a diuretic effect. Diabetic medicine sodium-glucose-co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors are diuretics. It is commonly prescribed in the management of type-2 diabetes. Sodium-glucose-co-transporter-2 is a protein in kidneys that has the function of reabsorbing glucose from kidney tubules. Consult complete information about SGLT2 inhibiters. SGLT2 inhibitors work by inhibiting the action of this protein. Diuresis (increased urine production) is the most observed side effect of SGLT2 ingestion.
How does Diabetic Medicine SGLT2 Inhibitors increase urine production?
The Mechanism Explained
Sodium-glucose-co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors such as empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and canagliflozin work on the specific transporter protein in the kidneys. Sodium-glucose-co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) is a transporter protein that brings about the reabsorption of glucose from renal tubules back into the bloodstream. As diabetic patients are already immune to the breakdown of glucose, excess glucose can aggravate the disease. SGLT2 inhibitors restrict the activity of this protein. Glucose tends to remain in the urine composition. More solute particles (glucose) in the urine create an osmotic force. Water from the surrounding blood vessels and tissues begins to move according to concentration gradient.
Excess glucose in the urine directs the movement of water (osmosis) through a partially permeable membrane to the lower concentration (urine). The movement of water into the urine creates water tension in the blood vessels and results in low blood pressure. On the other hand, excess water expels out from the body in the form of urine, causing dehydration.
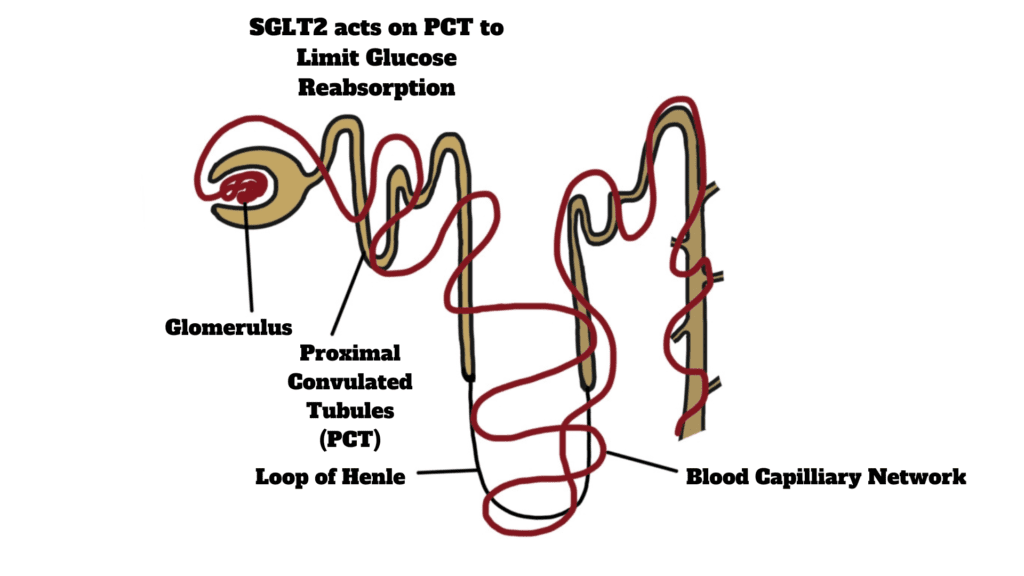
This whole mechanism has the purpose of lowering glucose concentration in the bloodstream by inhibiting its reabsorption.
Challenges Associated with Diuretic Diabetic Medicines
SGLT2 inhibitors can lead to severe complications due to dehydrating effect. Appropriate fluid consumption is required to manage fluid loss. Dizziness, dry mouth, and cognitive impairment are the symptoms of dehydration. Severe dehydration may prove fatal as the body needs an appreciable volume of water to carry out body mechanisms. Following entanglements could arise from the diuretic effect.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Water keeps the pace of electrolytes by controlling their concentration in intracellular and extracellular fluids. Loss of fluid is associated with loss of electrolytes. Crucial electrolytes, for instance sodium, potassium, and calcium, are integral in sustaining normal body processes. Calcium is indispensable in muscle contractions and neurotransmitter release. Sodium and potassium play a central role in nerve impulse transmission. Potassium, the most important electrolyte for heart health, should be in adequate quantities in body reserves. Potassium deficiency tends to affect heart rate and lead to arrhythmia. Learn how potassium imbalance can lead to arrhythmias.
Hypotension and Hypoperfusion
The low fluid content of blood reduces the blood volume when water moves out from the blood vessels into the renal tubules for normalizing glucose concentration (effect of SGLT2 inhibitors). Reduced blood volume lessens the blood pressure from normal (hypotension) and consequently leads to hypoperfusion. This, in turn, makes the cardiac output low. Reduced cardiac output is not able to nourish all body cells appropriately. Hypoperfusion is the condition when the blood supply to vital organs and tissues is insufficient to deliver oxygen and nutrients. Dire hypoperfusion can cause hypovolemic shock which seriously affects vital organs.
Genital Infections
High glucose concentration in urine affects genital health. High glucose concentration helps create an environment favorable to fungi and bacteria. Increased urine production makes the genital area warm and moist. Women are more prone to genital infections due to the sensitivity of their genital area. Yeast, such as Candida, is most likely to grow and can cause candidiasis. Similarly, bacterial intrusion results in bacterial vaginosis. General symptoms of genital infections include itching, discomfort, and abnormal discharge. In men, infection impacts the foreskin and glans with abnormal discharge and irritation.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) may commonly be associated with Type 1 diabetes. There is an increased number of reports associated with SGLT2 inhibitor intake and Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Diabetic Ketoacidosis results when there is increased production of ketones in the body as the result of fat metabolism. SGLT2 inhibitors augment the glucagon levels. Glucagon (a hormone secreted by the pancreas that works antagonistically to insulin) stimulates the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream.
SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended for patients with type 2 diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, insulin production is either low or cells become insensitive to glucose. Glucose insensitivity makes the cells not take glucose from the bloodstream. The body takes this signal as there is low glucose in the blood. In response to that, it starts secreting glucagon. SGLT2 inhibitors amplify glucagon production and at the same time, increase the breakdown of fats for energy production. Inability of cells to absorb glucose can make them strive for energy.
Body metabolism takes an alternative path and starts producing ketones for energy production. The body uses stored fats for the ketogenesis, than can result in elevated ketone levels. The breakdown of fats releases ketones in the body, resulting in high ketone content in the blood.
This is Not a Medical Advice
Diabetic and other medications can have diuretic effects. However, it is advised to pay heed to the medical advice from a medical doctor before targeting any medicine. This blog only provides the conceptual information about how some medications can have diuretic effects.