What are Teratogens?
Teratogens are agents or substances that have the potential to disrupt the normal development of an embryo. They are not harmful substances in general but can induce malformations or developmental issues when introduced during gestation. Teratogens are harmful substances for pregnant women as they interfere with fetal development, provoking congenital disorders.
Teratogens are not only the cause of congenital disorders. Other factors such as genetics, chromosomal mutations, and nutritional deficiencies also can introduce congenital disorders. Maternal age and father’s genetic makeup also play a pivotal role. Here, we are going to understand environmental factors that include the teratogens.
Congenital disorders like Down’s syndrome, Edward syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, or other defects like sickle cell anemia are the result of genetic and mutational abnormalities. The environment does not play any role in the development of these disorders. Apart from these, many other congenital disorders like Fetal Alcohol Syndrome(FAS), microcephaly, and thalidomide complications are purely due to teratogenic substances. Medications are used to treat congenital disorders temporarily such as PGE1 is used to to treat ductus-dependent lesions in congenital heart defects. The ultimate treatment is surgery or gene therapy for such diseases. For that reason, understanding teratogens and the congenital disorders related to them is momentous.
Examples of Teratogens – Potential Threats for Causing Congenital Disorders
Following are the teratogens explained with the congenital defects they are infamous for.
Drugs and Medications
Several medicines can be teratogenic based on their after-effects when taken during fetal developmental stages. Following are the two examples of such teratogenic drugs.
Thalidomide Complications: Thalidomide was a widely used drug in the late 1950s. It was used to treat nausea or morning sickness in pregnant women. It proved very effective in serving the required purpose. However, after some time, observations revealed that a number of children are born with limb abnormalities. Through studies and surveys, it was noticed that a great ratio of children with limb abnormalities are born to women who had taken thalidomide during their gestation period. Scientific studies, later on, revealed that this drug interferes with limb development in fetuses. Ergo, it was banned later and international practices were followed to ban the transport and marketing of this drug across borders.
Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin (Accutane) is a potential teratogenic substance. While its teratogenicity is well-known, it is still in use. Why? Because isotretinoin is a renowned drug for treating severe acne. Isotretinoin has made it fame for its effectiveness in treating specific kinds of acne. That’s why it is still in use but under strict measures. In the 1980s, its teratogenic feature began to emerge. It is known for causing congenital heart defects, microcephaly, and other brain abnormalities. Later on, the government introduced pregnancy-prevention programs to spread awareness of its teratogenic effects. The purpose of this program is to prevent pregnancies while taking the treatment of isotretinoin. In 2002, the FDA modified the program as “iPLEDGE” to perform the same task.
Alcohol – One of the Potent Teratogens
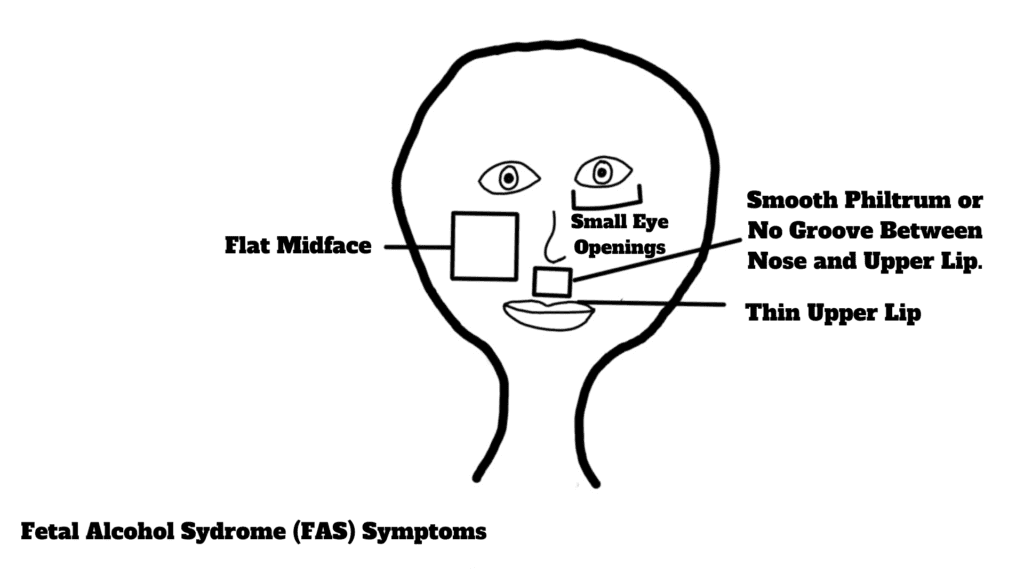
Alcohol is infamous for causing Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs). FASDs is a collective term used for congenital defects associated with alcohol consumption in pregnant women. Alcohol crosses the placental barrier and meddles with fetal development. It causes severe physical abnormalities and behavioral and cognitive impairments. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is the most severe form of FASDs with distinguished facial features. FAS is characterized by distinctive facial dysmorphia. A smooth philtrum ( groove between the nose and the upper lip), thin upper lips, and small eye openings are the keynote symptoms of FAS. Other forms of FASDs are also notorious for causing behavioral and cognitive disabilities but they are not associated with distinctive facial features like FAS.
The severity of FAS also depends upon the quantity of prenatal alcohol exposure. A study was published in the journal “Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research in 2014, with the title “Dose-response effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on facial morphology”. This study explored the relationship between prenatal alcohol exposure and the severity of facial features associated with FAS. General results suggested increased risks of facial dysmorphia with high alcohol consumption.
Tobacco Smoke and Nicotine
Smoking provides potent teratogens that affect fetal development badly. Tobacco and nicotine are the paramount teratogens affecting fetal development. Nicotine is a vasoconstrictor and constricts the blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. The fetus survives badly due to the lack of necessary oxygen and other supplies. Smoke also contains carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide has more affinity to attach with hemoglobin as compared to oxygen. Inhalation of carbon monoxide leads to severe hypoxia.
The gross effects of tobacco smoke on fetal development result in respiratory problems in the fetus, preterm birth, and low birth weight. It is not necessary that only a mother’s smoking causes congenital disorders, but the father’s smoking habits also impact fetal health. This area of research is not well-known, but the father’s smoking causes variations in his genetic makeup and can indirectly affect the fetus.
Some Infections Can Also be Teratogens
Certain infections can be teratogenic. It means they have the potential to alter normal fetal development when pregnant women are affected by them. Such infections are many, but here is an overview of two of them. These are the most common infectious teratogens.
Rubella: Rubella virus also known as German measles. It is a potent teratogen when it infects a pregnant woman. Rubella virus stains can interfere with the critical stages of organ development. It can result in cataracts, hearing loss, and heart defects. These are only the physical symptoms of Rubella infection, but at the same time, they also cause intellectual disabilities and cognitive impairment.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV): CMV affects the fetus severely when the mother acquires CMV as a primary infection. CMV poses birth defects to the developing fetus, affecting hearing, eye health, and intellectual disabilities. CMV is the leading cause of congenital hearing loss. There is also a possibility of CMV infection even when it does not infect the mother during the gestation period. In this scenario, CMV is the dormant form in the mother’s body and reactive during fetal developmental stages. Reactivation of CMV is less harmful than the primary infection.
Radiations
Radiations (both ionizing and non-ionizing) have the potential to impact fetal health drastically. Ionizing radiations are much more harmful both to mother and fetal health. They can cause ionization of molecules and increase the formation of ions in the body. The ionization of biological molecules causes serious chromosomal defects in the developing fetus. It is advisable to mitigate any contact with radiation during pregnancy as their effects persist in the generations (if they cause mutations in germ cells). Medical imaging and X-ray exposure should be avoided during pregnancy. Such tasks can be postponed to alleviate the chances of congenital disorders.
Heavy Metals
Heavy metals such as mercury and lead are disreputable for causing congenital defects. The most common and harmful form of mercury is methylmercury. Methylmercury is mainly obtained from contaminated seafood and fish consumption. Fish at the top of the food chain have elevated levels of methylmercury in their body composition due to the ingestion of other small fish. Fish like sharks or tuna, are predatory and have an accumulation of methylmercury. As for lead, its major source is paint-based lead.
Industrial settings working with heavy metals offer higher chances for lead exposure. Lead and methylmercury affect the brain development of the fetus. Lead is more renowned for interfering with cell division and differentiation of the fetus. Thus, both are detrimental to fetal development.