Introduction;
Low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia) can have slight to severe effects on the body’s functions. Low calcium levels do not only affect physical health but also contribute to variations in mental health. Calcium ions are the bottom line in sending electrical signals between nerve cells. Low calcium levels disturb the normal connectivity of brain cells (neurons), affecting the cognitive development of a person. How low calcium levels affect mental health is another story, in this blog, we’ll discuss how variating calcium levels affect physical health. Calcium is a cation with the valency of giving 2 electrons (Ca2+). Calcium ions play indispensable roles in coordinating electrical impulses, smooth and skeletal muscle contractions, neuromuscular connections, etc. Low calcium levels variate these normal happenings and can have apparent signs on the body.
9 Physical Signs of Low Calcium Levels
Following is the explanation of 9 physical signs of low calcium levels and what is the background study of their occurrence.
1. Muscle Twitching or Frequent Muscle Contractions
Muscle twitching or muscle excitability occurs in the event of low blood calcium levels. Calcium ions monitor the release of neurotransmitters at neuromuscular gaps (space between neurons and muscles). When the brain sends electrical signals for a muscle to contract, nerve cells take this signal all the way through the brain to the muscle receptors. Just before a muscle perceives the signal, deficient calcium levels can hinder this activity. Low calcium levels cannot make the synaptic vesicles (that contain neurotransmitters) fuse with the membrane and release neurotransmitters in the neuromuscular gap. You can also read the release process of the serotonin (neurotransmitter) release that multiplies the feeling of a happy mood. This blog will help in the thorough understanding of calcium ions’ role in nerve impulse transmission.
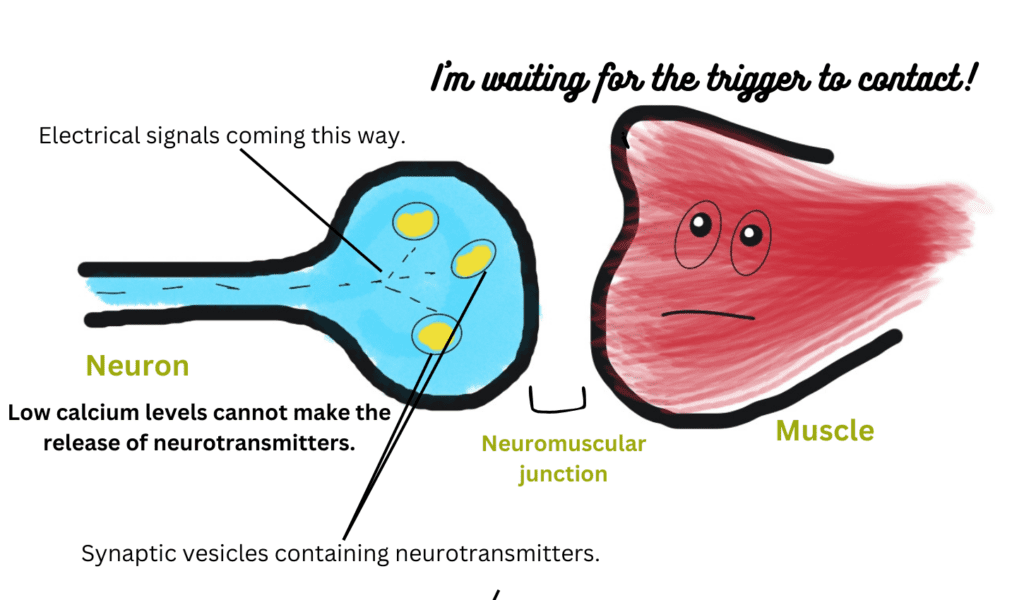
Sticking to the topic, the brain is sending signals to the muscles, but the dropping calcium levels cannot make them contract. The brain perceives this lack of contraction and sends more and more signals in a repetitive manner to make the muscles contract. This leads to the hyperexcitability of muscles and causes muscle twitching. Muscle twitching can be defined as repetitive, hyper, intense, jerky contractions of muscles. Facial muscle contractions are most common in the case of low calcium levels in the blood.
2. Muscle Spasms or Cramps
Muscle spams occur when muscle contractions are prolonged due to the inability of muscles to relax. Both muscle contractions and relaxations depend upon calcium ions. Calcium ions change the 3d conformation of muscle proteins (myosin, actin, troponin, and tropomyosin) and make the muscles contract. Similarly, in order for a muscle to relax, these proteins release calcium ions back into the sarcoplasm of muscles. Low calcium levels disrupt this activity, prolonging their contracting state. Muscle cramps are painful for some people and are normal. But, critically low calcium levels can cause muscle spasms with greater frequency and time period.
3. Weakness or Fatigue
Low blood calcium levels cause weakness and fatigue either by changing bone integrity or reducing the chances of muscle contractions. Low calcium levels lessen muscle contractility by making them less responsive to electrical signals. When muscles are not actively used, they become susceptible to muscle atrophy. If we do not utilize muscles with a routine, they become less effective gradually. Soon, a time comes when muscles become useless due to abandoning them. It causes fatigue and weakness in the whole body, making routine processes difficult to do.
4. Weak Enamel and Cementum of Teeth
Low calcium levels have bold effects on tooth health. In fact, one can say that dental health gives the most prominent signs of low calcium levels. The enamel of the tooth which is its outermost layer is made up of a hard matrix, containing hydroxyapatite crystals. Hydroxyapatite crystals have calcium in the form of calcium phosphate with calcium hydroxide. Both give a hard touch to the aura of teeth. Cementum is not as hard as enamel. It covers the tooth root and integrates the tooth into the jawbone mass. It is mainly made of tricalcium phosphate. Similarly, dentin that is present beneath enamel and cementum also contains hydroxyapatite crystals.
So, insufficient calcium levels affect tooth health with great affinity. As almost all the tooth layers contain calcium as the main component, like bones and nails, low calcium levels are detrimental to teeth health.
5. Compromised Skin Barrier
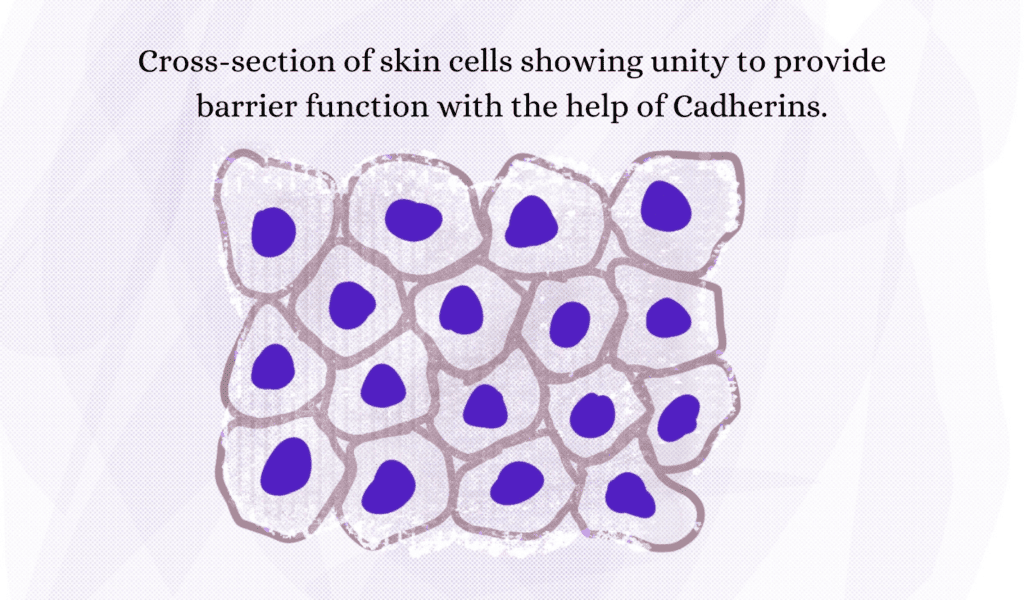
Calcium ions maintain the moisture and smoothness of the skin by keeping the skin barrier crisp. Calcium ions help synthesize special skin cells called cornified skin cells that pursue the guarding of the skin by environmental stressors. Cornified skin cells demand calcium ions for their formation and development. Moreover, cell-to-cell linking of skin cells upkeeps the more solid layer and functions as a unit. Calcium ions keep this cell-to-cell adhesion up to date and let the skin cells fight pollens collectively. It’s more like united we stand, divide we fall. Cadherins are the cells that keep cell-to-cell adhesion in check. Calcium ions facilitate cadherins in their function. Therefore, low calcium levels will speak out loud by comprising this more solid barrier of skin cells.
6. Osteoporosis in Bones
Bones have calcium in the same form as nails and teeth. Calcium Phosphate makes the hard part of bones and adds it to its compactness. Osteoporosis (porous or weak bones) happens in falling short of calcium levels. Vitamin D is a must-have ingredient for depositing calcium into the bones. Without sufficient vitamin D molecules, the bones can’t get calcium for their bony matrix. Hydroxyapatite crystals mineralize the bones by their capacity to hold a good quantity of minerals, including calcium phosphate.
7. Irregular Heart Beats
Calcium ions coordinate the movement of sodium and potassium ions through cardiac muscle membranes. Like in other muscle cells, calcium ions control the cardiac muscle contractions. Although calcium ions directly do not participate in maintaining heartbeats, they affect the movement of potassium ions. Potassium ions keep the heart beating at pace. Calcium ions also modulate the electrical signaling of the heart’s pacemaker, sinoatrial node (SA node). Ergo, calcium levels below normal will ruffle the electrical rhythms of the heart, leading to arrhythmias.
8. Weak and dry scalp
Calcium ions keep the hair follicles up to date. Hair follicles are the cells under the hair scalp that nourishes hair strands by providing nutrients and appropriate environment. Calcium ions play their part in checking the health of these follicles and in turn, create thick and robust hair strands. Moreover, calcium ions also maintain the sebum production that prevents dryness and flake formation. Low calcium levels create dry, weak, and flaky hair scalp. Such a hair scalp is more susceptible to minute environmental changes. As a result, the weak hair scalp and weak hair follicles produce thin and appalling hair.
9. Difficult Swallowing (Dysphagia)
Low calcium levels cause difficulty in swallowing food down to the stomach. Muscles that stimulate the swallowing of food, such as pharyngeal and esophageal muscles, require adequate calcium levels for their contractions. Calcium ions do not only govern the contractions of skeletal muscles, but they also monitor the activity of smooth muscles. Therefore, smooth muscles of the swallowing process respond bluntly to the drop in calcium levels. Inadequate calcium levels, as explained above, also upset the perception of electrical signals sent by the brain. Such multiple reasons, when combined, cause difficulty in swallowing food (dysphagia) or make the swallowing muscles take more time to pass the food.
What Can We Do To Preventing These 9 Symptoms of Low Calcium Levels?
To prevent these 9 physical signs of low calcium levels, one has to keep his calcium levels in check. Consuming foods that are affluent with high calcium content is the most helpful and instant strategy for managing low calcium levels. Foods such as milk, yogurt, other dairy products, green vegetables have substantial amounts of calcium. Read more about the foods that contain calcium as the main nutrient. Furthermore, what if you’re taking enough calcium diet, but still your calcium levels are below normal?
Well, that can be due to low vitamin D levels in the body. Minimal sunbaths in the routine helps supervise vitamin D concentration in the body. It’s also a myth that sunlight produces vitamin D in the body, yes, to some extent it’s true. But, sunlight does not actually produce Vitamin D. The story is a little bit curvy. Anyhow, whatever the story behind vitamin D production, its presence is mandatory for absorbing calcium into the blood. Without vitamin D, the body’s mechanisms are not efficient enough to absorb calcium from the intestines into the diet.
So, it can also be the underlying cause of abnormal calcium levels in the blood. Besides taking a healthy natural diet, certain medications and supplements also aid in managing calcium levels. These chemicals contain calcium in the form of calcium carbonate, calcium citrate, or calcium chloride. These salts bring the calcium concentration to normal. But, a natural diet and enough vitamin D would be more organic way to manage low calcium levels.
In the case of medications or supplementation, a bit of professional advice is recommended. Self-prescribed intake of these medical compounds can have adverse effects, a medical doctor would guide better about their proper dosage and use.





Very productive info, knowledge booster. Keep it up ✨
Thanks Awais for your nice words.
“Hello there! I recently noticed that you’ve taken the time to visit my website, and I wanted to express my gratitude by returning the favor. As I’m constantly seeking ways to improve my site, I believe it would be beneficial to incorporate some of your ideas into my design and content strategy. Your input would be greatly appreciated, and I’m open to any suggestions you may have. Thank you for your interest, and I look forward to hearing from you!”
Feel free to let me know if you need further assistance or if there’s anything else you’d like to add or modify!